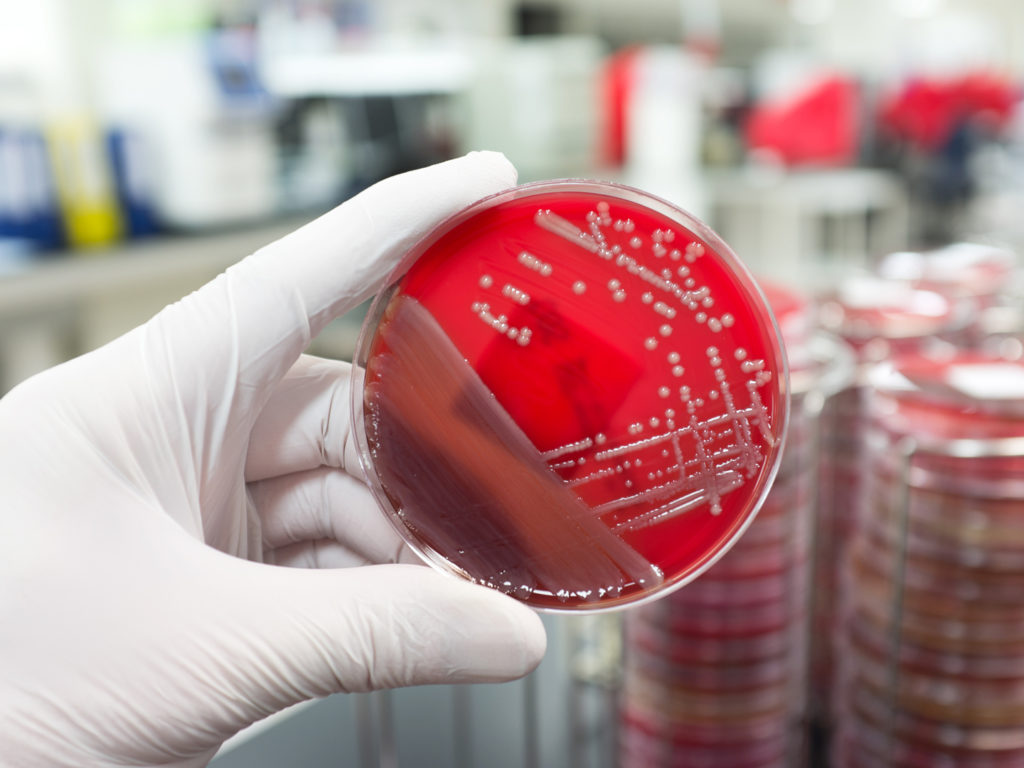
Microbial culture is a method of growing microorganisms in a controlled environment. It is very important to ensure the growth of only the intended microorganisms and have a pure culture free from other types of microbes as the culture is very susceptible to contamination by other microorganisms. The air that we breathe is also a source of contamination, other types are handled in a controlled manner. This technique is the foundation for all molecular biology techniques including diagnostic techniques which use microbial cultures to grow the intended microbes and then study their characteristics. For example, a throat culture means a sample is taken by scraping the lining tissue of the throat and the sample is taken in a medium and cultured to screen for a particular microorganism like Streptococcus pyogenes.
In pure culture, there will be no other species or even the close variants of the microorganisms. For example, in a culture of E.coli K12 bacteria, there cannot be even E.coli O 121. A pure culture can originate from a single cell also. For the ease of handling the culture, they are studied on a gel call agar – a biopolymer obtained from seaweed.

Microbial culture on solid and liquid media
There are different organizations around the world which provide microbial cultures. The American Type Culture Collection or ATCC is an organization based in the USA whose products are considered as a standard in the scientific community. It collects and stores various strains of microorganisms and distributes references for microorganisms and cell lines for research and development purposes. Its cultures are distributed to around 150 countries and have the largest culture collection in the world. They have a wide range of collection including cell lines, microorganisms and bioproducts. ATCC’s microorganism collection includes a collection of more than 18,000 strains of bacteria, as well as 3,000 different types of animal viruses and 1,000 plant viruses. In addition, ATCC maintains collections of protozoans, yeasts and fungi with over 7,500 yeast and fungus species and 1,000 strains of protists.
In the scientific community, ATCC is considered to be one of the most reliable sources of authentic cultures and they also have a wide variety of cultures including algae, viruses and protozoa. ATCC does continuous research for the preservation, propagation and characterization of cultures through its in-house facility and also by collaboration with other culture collection centres.
But sometimes it easy and is preferred to get the culture from one’s own country as there are various law and customs regulations during import and also the risk of contamination or sometimes the risk of the infection also. And moreover, all the local collection centres will provide the cross-index number with those from other cultural centres.
There are many options if you are looking for getting cultures in India. A list of the centres is given below.
| ABRC | Anaerobic Bacterial Resource Centre |
| AYL | WHYLABS RESOURCE CENTRE FOR MICROORGANISMS |
| BDU | National Facility for Marine Cyanobacteria |
| CCDMBI | Culture Collection, Department of Microbiology |
| CIPDE | Collection of Insect Pathogens, Dept. of Entomology |
| DBV | Division of Standardisation |
| DMSRDE | DMSRDE Culture Collection |
| DUM | Delhi University Mycological Herbarium |
| GFCC | Goa University Fungus Culture Collection and Research Unit |
| ITCC | Indian Type Culture Collection |
| MCC | Microbial Culture Collection |
| MCM | MACS Collection of Microorganisms |
| MPKV | Biological Nitrogen Fixation Project College of Agriculture |
| MTCC | Microbial Type Culture Collection & Gene Bank |
| NCDC | National Collection of Dairy Cultures |
| NCIM | National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms |
| NFCCI | National Fungal Culture Collection of India |
| NIICC | NII Microbial Culture Collection |
| NMCC | North Maharashtra Microbial Culture Collection Centre |
| NTCCI | Culture Collection, Microbiology and Cell Biology Laboratory |
| RRJ | RRL , Jammu INDIA |
| UMFFTD | Food and Fermentation Technology Division, University of Mumbai |
| VBCCA | VISVA-BHARATI CULTURE COLLECTION OF ALGAE |
| VPCI | Fungal Culture Collection |
There are 27 culture centres in India registered with the world data centre for microorganisms (WDCM) which is more than the number of centres in the united states of America (24). Microbial Type Culture Collection & Gene Bank (MTCC) based in Chandigarh and the Microbial Culture Collection(MCC) at National Centre for Cell Science Pune are two good options for culture collection in India and are the only centers in India to get recognition as International depository authority(IDA) from WIPO, Geneva, Switzerland. In 2007, Depart of biotechnology (DBT) took an initiative to undertake a screening project which involved 9 major research institutes and a pharmaceutical company (Piramal life sciences limited). The isolated strains were deposited at the MCC and the DBT mandated that all the isolates generated in this project would be made available at this collection for future use by others who wish to exploit them for biotechnological purposes. MCC holds more than 150,000 bacterial strains isolated under DBT’s Microbial Prospecting project.
With so many local culture collection centres in India and a holding of more than 1,50,000, it would be preferable to get the culture from the local centres. Some of the centres also have IDA recognition, meaning that they have quality like any other major centre in the world. One may go for import preferably only if the intended strain is not available in the local centres.