In present times, when there are several pathogenic microbes dispersed across various environments, food quality is a major concern. We often find that aseptic packaging methods such as tetra packs and canned foods are unsuccessful in preserving food over a period of time. Finding a suitable chemical preservative which does not alter food quality, and is safe for consumption, is not an easy task.
As various bacteria grow in environments with multiple species of bacteria, they produce Bacteriocins. These bacteriocins are anti-bacterial substances which kill similar, or closely related bacteria. These are produced due to competition over available food substrates. Microbiologists around the world have been researching the possibilities of using these bacteriocins as food biopreservatives, to inhibit the growth of food pathogens.
A. Ashwitha and fellow researchers at the Sri Ramaswami Memorial University, India, have evaluated the antimicrobial activity of a bacteriocin produced by Bacillus sp against two aquatic pathogens, Salmonella spp and Vibrio spp, which were isolated from infected marine fish.
Electron micrograph of Bacillus subtilis
(Source: https://www.nyrture.com/blog/2015/5/23/the-subtle-beauty-of-bacillus-subtilis-part-ii)
To study the biopreservative action of bacteriocin, tissues of infected pomfret fish and squid with Salmonella and Vibrio were treated with bacteriocin produced by Bacillus subtilis (KY808492). The treatment was carried out in different storage conditions (at -4°C and -20 °C) for 30 days, where the microbial load of the tissue samples was estimated once, every 5 days. It was observed that bacteriocin activity gradually reduced the numbers of the two pathogens in both the storage conditions in a time-dependent manner.
Bacterial bacteriocins produced are generally peptides or proteins in nature, and due to sensitivity against protein cleaving proteases, these may be digested. Hence, there is no danger from their ingestion and they can be used as natural preservatives in food products. Bacteriocins have been incorporated in foods in traditional methods since old times, by addition of lactic acid bacteria (producing bacteriocins), to various food products such as cheese, yogurts and Portuguese fermented meat. Due to heat stability and pH tolerance, it can withstand heat and acidity/alkalinity of food during storage conditions. There are even studies that show that bacteriocins provide the benefits of probiotics, which are microorganisms consumed to help balance the intestinal flora.

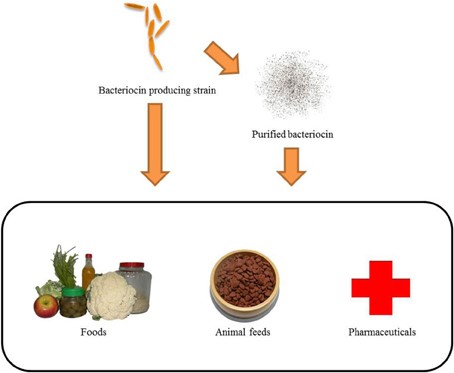
Applications of bacteriocins
Source: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00241/full
Although many types of bacteriocins such as subtilin, cerein, thuricin, plantaricin etc. have been isolated and characterized, they are still in a process of getting commercial status to be used as food preservatives. So far only one bacteriocin, Nisin, has been given approval as a preservative to be added in food items commercially. Nisin has been concentrated as Nisaplin, which is used as a preservative in milk, dairy products, canned foods, cured meats and in other segments of fermentation industry, since it inhibits virtually all gram-positive bacteria in food.
From these studies we believe, the day is not far off when chemical preservatives will be replaced by biopreservatives, completely or partially in the food, ultimately providing safer and healthier food to consumers.
References:
1] Ashwitha, A., Thamizharasan, K., Vithya, V., & Karthik, R. (2017). Effectiveness of Bacteriocin from Bacillus Subtilis (KY808492) and its Application in Biopreservation. Journal of FisheriesSciences.com, 11(3).
2] Gautam, N., & Sharma, N. (2009). Bacteriocin: safest approach to preserve food products. Indian journal of microbiology, 49(3), 204-211.
3] Yang, S. C., Lin, C. H., Sung, C. T., & Fang, J. Y. (2014). Antibacterial activities of bacteriocins: application in foods and pharmaceuticals. Frontiers in microbiology, 5.