Plastic, a miracle of the 19th Century, has become a highly hazardous litter of the 21st Century. Due to the cost-effectiveness, the robust, highly durable plastic products are widely used in day-to-day life. However, it is the major contributor to global pollution. The manufacturing of plastic requires the substantial use of valuable resources of oil and a significant quantity of toxic chemicals. Plastic products are derived from natural and organic material, including crude oil, cellulose, coal, and natural gas. Polymerization and polycondensation are the two main processes used to produce plastic products from the complex mixture of compounds. The manufacturing of plastic products is economical; however, its recycling is more costly than production. When plastic is disposed of in the environment, either in oceans or in a landfill, it leaches out harmful chemicals causing damage to the entire ecosystem. The proper disposal of plastic waste is today’s topmost global priority.
More than 300 million tons of plastic are produced annually across the globe using fossil fuels, which eventually gets thrown either in a landfill or the ocean for disposal, causing hazards to the environment. More than 8.8 million tons of plastic enter the ocean through multiple outlets such as rivers and cause severe damage to the marine ecosystem. A large number of marine animals such as turtles and fishes have ingested plastic waste. Many of the marine species have vanished or died due to plastic ingestion.
There are numerous plastic items including plastic bottles and utensils that are responsible for severe pollution problems. The single-use plastic bottle used for coke, cold drinks are a big threat as the disposal of these bottles is difficult, and almost all of them are not recyclable. Many of the products are used for a very little period, sometimes only once.
To minimize the harmful effects of plastic waste disposal on the environment, researchers and industries are working on developing a sustainable, eco-friendly solution to the plastic bottles.

Bioplastic is emerging very rapidly as an alternative to conventional plastic. Bioplastic or bio-based plastic is a plastic made up of plants or other biological materials such as microorganisms. Plant-based plastic is one of the popular, cost-effective forms of bioplastic. As the name suggests, plant-based plastic is made by extracting sugar from plants such as corn, potato, sugarcane, and wheat. The plant-based plastic is made in a biorefinery; where the extracted sugar is converted into polylactic acid, which is further used to make plastic. Polylactic acid plastic is used in food packaging. Plant-based plastic can be a better option for single-use applications that are food-oriented such as bottles, straws, utensils, etc.
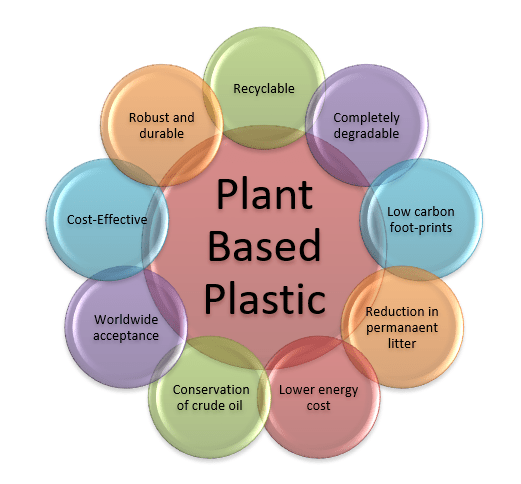
Benefits of Plant-Based Plastic Bottles:
Plant-based bottles are sustainable and cost-effective. They are sturdy, and durable similar to that of the conventional plastic bottles. Plant-based bottles require a lesser amount of energy for production. They are recyclable and can be completely degraded back to carbon dioxide and water. These bottles can be decomposed of in one year in industrial or home-based composters, or a few years if dumped in normal outdoor conditions. They can be produced completely without monomers and additives that are harmful to humans. A very few pollutants are used during the manufacturing process of the plant-based plastic bottles.
Many manufacturers are now moving to more sustainable approaches when food packaging is concerned. Avantium, a biochemical company in the Netherlands in its pioneer project plans to develop plant-based plastic bottles that will degrade within just one year. The manufacturer expects to bring the product in the market by 2023. Furthermore, the company plans to make use of biowaste to derive plant sugars, so that the global food supply chain remains unaffected. Carlsberg and Coca-Cola are the two big brands that are supporting Avantium, for “All Plant” drink bottles.
As fossil oil is limited, the use of plant-based plastic or bioplastics is expected to surge soon. However, plant-based plastic is made from sugar and starch derived from the harvested crop that otherwise might be consumed as a food. Hence, the making of plant-based plastic should not reduce the land available for food production and decrease food quantity. It should not increase deforestation and increase emissions. If these aspects are dealt with proper care and management, plant-based plastic could be a more promising way of maintaining the benefits of conventional plastic along with the elimination of its disadvantages.
References:
- https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2020/may/16/the-end-of-plastic-new-plant-based-bottles-will-degrade-in-a-year
- https://www.ecowatch.com/plastic-bottle-plants-sustainability-2646025779.html?rebelltitem=5#rebelltitem5
- https://www.onegreenplanet.org/environment/new-plant-based-bottles-made-from-plant-sugar-degrade-in-a-year/
- https://www.forthebettergood.com/
- https://www.greenbiz.com/article/rise-plant-based-plastic-packaging
- https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/2018/11/are-bioplastics-made-from-plants-better-for-environment-ocean-plastic/
- https://www.coca-colacompany.com/sustainable-business/packaging-sustainability
- https://www.natracare.com/blog/plant-based-plastics-perfect-solution-or-huge-problem