The sun being a star provides the ultimate source of energy that runs our solar system, especially our planet. It is because of this star situated at an exact distance which makes earth habitable. However, that isn’t all, the sun’s energy known as solar energy is the most potent source that can drive all forms of life and work on this planet.
Not just the basic natural cycles but also modern equipment and devices which requires electricity can be dealt with solar energy. This huge pool of energy travels as photons which can be entrapped in silicon or other material coated device called solar panels. It is these panels which form the basis of a renewable way of utilizing solar power.
Solar Panel Technology & Its Utility
Now, this solar panel technology has come a long way since its inception 60 years ago. Nowadays, there are methods to manufacture more stable and inexpensive solar cells. These modern-day solar cells have a greater Yablonovitch Limit. Hence, a higher thermodynamic limit ensures they entrap photons for a longer period in the semiconductor. This, in turn, is good for productivity and longevity.

(Source : https://images.app.goo.gl/uZQDcsPC5dJfBhsT8)
Solar panels are beneficial for households and businesses as it reduces the dependency on electricity. With solar panels installed in a building’s roof you can capture the sun’s energy as photons and use it to generate electricity for the whole household by connecting to it.
How did it reach its present form?
Now, the question is how such technology developed over the years. It’s years of theoretical and practical inventions which lead to this. Although a relatively new technology which started its journey about 6 decades back, yet its connection can be drawn up to the photoconductivity discovery about a century back. But we won’t start that early rather we will discuss the basics of solar panel evolution.
- The first solar cell was created by coating selenium on a gold layer by New York inventor Charles Fritts in 1883. This one had 2% efficiency as opposed to 20% that we see today.
- In 1887, with the discovery and explanation of the photoelectric effect by Hertz and Einstein respectively, we got the idea of converting trapped photons to power (electrons).
- After this, there was a dull period. More than 50 years after Einstein’s Photoelectric effect Nobel Prize for the first commercial solar was developed in 1953. These Silicon Solar Cells developed by Bell Laboratories Physicists were 6% efficient.
- By 1956 Western Electric began selling commercial licenses for silicon solar cells, although the cost of such cells was high.
- Two years later, the US govt. utilized sat energy to power a satellite called vanguard1 which has made 197000 revolutions around earth. This move was significant in drawing more attention to solar cell research and productivity analysis
- Finally, nearly 10 years later in the early 1970s solar cells were made from low-grade silicon which lowered costs from 100$ per watt to 40$ per watt. This resulted in large scale solar energy initiatives such as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in 1977.
- In 1982, the US Govt. created the first solar park in California which generated 1 megawatt of power per hour, when fully operating. This was a significant milestone as it could produce enough power to light a 100-kilowatt light bulb for 10 hours.
- A second park came up in 1983 which generated 5.2 megawatts. However, solar energy use dwindled as the oil market gained strength and became cheaper again
- In 1995 came RV Solar Panels which was used to empower recreational vehicles
- 4years later, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory revolutionized Photovoltaic Conversion to produce a new solar cell with 30% efficiency. These cells were made of gallium indium phosphide and gallium arsenide.
- By the time we reached the turn of the century, thin-film solar cells with 32% efficiency were underway.
- Ultimately, DIY Solar Panels hit the market in 2005 and by 2015, flexible printed solar panel strips came to the market. The strips are a great choice as it reduces the problem of huge equipment. A single strip produces 50watts energy per square meter and has an efficiency of 20%. This has led to the widespread use of solar panels across the globe, especially in developing countries.
This is how solar cells evolved but it hasn’t stopped. It’s reaching new heights with more path-breaking research.
Where is it moving now?
Nanoparticles Enhanced Solar Cells
Now, we are moving towards a regime where even the sun isn’t needed for energy generation. A team of researchers from Australian National University and the University of Berkeley, California came up with nanoparticles coated solar cells. They discovered that nanomaterials have a property called magnetic hyperbolic dispersion, which makes it glow when heated. Now, if we combined this with thermophotovoltaic cells, heat can be turned into electricity without using photons of sunlight.
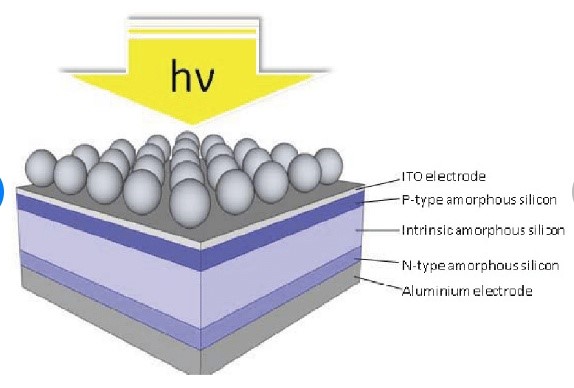
(Source : https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Geometry-of-a-nanoparticle-enhanced-thin-film-amorphoussilicon-solar-cell-The_fig1_267762563)
- Geo-patterned Solar Cells
Another group of researchers from the North-western University suggests a simple mathematical algorithm derived scattering of the layers to maximize entrapping of photons. According to their research, the newly designed organic solar cell allows light to first enter through a 100-nanometer-thick “scattering layer”. Now, this is a geometrically-patterned dielectric layer designed to maximize the amount of light transmitted into the cell. The light is then transmitted to the active layer, where it is converted into electricity.
All this shows how useful solar cells can be in the future. At a time when climate change is wreaking havoc and fossil fuels becoming obsolete, solar power is our only hope.
References:
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/01/130125111358.htm
- https://www.solarpowerauthority.com/a-history-of-solar-cells/
- https://www.fortum.com/about-us/our-company/our-energy-production/solar-power-unlimited-source-energy
- https://blog.nationalgeographic.org/2012/05/30/the-evolution-of-solar-technology/
- https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/89364-the-evolution-of-solar-power-infographic