Drug discovery is a process by which a new drug or candidate for medication is discovered or synthesized. Drugs have a recuperative ability and hence its discovery becomes a modus operandi. Previously drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or in serendipitous discovery, just how penicillin was made. This article describes drug discovery and its development in detail. Our aim is to help people from any discipline understand this concept distinctly.
Modern drug discovery involves the identification of target molecules (disease inducing agents), and then drug molecules that can work against these targets are designed, their potency/efficacy is first checked in the lab. Those drug candidates which turn out to be effective in the lab are then tested on animals for their potency, metabolic stability and bioavailability. A few drug candidates pass through this preclinical phase; these are subjected to clinical trials and FDA approvals.
Billions of dollars are invested for this process. The United States is the major investor when it comes to drug discovery. The top pharma companies in the US including Orphan drug, Sanofi, Bayer AG, Biogen, Eli Lily, Amgen, Abbott Laboratories, Novartis, etc have a huge impact globally. Speaking about pharmaceutical companies in India, Actimus biosciences, Advinus therapeutics, Chembiotek, GVK Biosciences, Ranbaxy Life Sciences, Reliance Life Sciences, Syngene are amongst the top establishments which are leveraging a lot of investment in Research development.
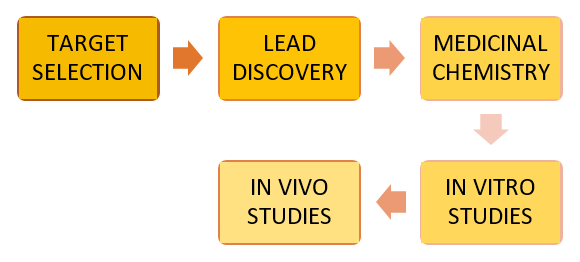
The Steps Involved in Drug Discovery:
- TARGET SELECTION:
Target selection in drug discovery is defined as the decision to focus in finding an agent with particular biological action that is anticipated to have therapeutic utility. Furthermore, this process is carried on with target identification (which means identification of causative agent) and target validation (to prove that the target molecule can provide therapeutic effect to respective disease). Target identification can be done on following basis:
- Cellular and Genetic Targets- Involves identification of certain cellular sites which can act as therapeutics, ex- vaccines
- Genomics- This includes studies based on DNA/RNA, like genome mapping, etc.
- Proteomics- Is the systematic high through put separation and categorization of protein within biological system.
- Bioinformatics- it involves in-silico studies of protein structures.
- LEAD DISCOVERY:
Lead discovery in pharmacology means designing the leading compound which has remedial effect against the target agents. Such compounds need to be modified to fit better to the target. This process involves further steps:
- Synthesis and Isolation
- Combinatorial chemistry (Optimizes targets affinity and selectivity – reduces drug toxicity and side effects)
- Assay Development- Used for measuring drug activity.
- High Throughput Screening- picking up drug targets against selection of chemicals
- MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY:
Medicinal chemistry has undergone a change in its paradigm since past 30 years. This process marks the already known or existing drug, bioactive natural products or biological mediators. It is a discipline with intersects the synthesis of organic chemistry and pharmacology. This process involves:
- Library development- This helps in high throughput screening of targets from stored chemical associated database.
- SAR (Structure Activity Relationship) studies- Enables to make more active compound.
- In Silico Screening- Helps in finding structures that are most likely to bind to the target drug
- Chemical synthesis- Helps in production of lead compound.
- IN VITRO STUDIES:
This process involves biological analysis performed in laboratories inside a glass tube. Examples: Cell derived from multicellular organism, subcellular component (ribosomes), Purified molecules (DNA/RNA). This Step involves:
- Drug Affinity and Selectivity
- Cell Disease Model- selective cells which are engineered to model the genetics of a specific patient or population.
- MOA (Mechanism of Action)
- Lead Candidate refinement- Optimizing chemical leads for further clinical trials
- IN VIVO STUDIES:
This is the Step when drug testing is done on whole, living organism. Organisms could be model animals. This is a crucial step which gives us the information about drug’s metabolic profile, toxicology, and drug interaction with other molecules. Also, side effects of any drugs can be checked in this very step. This step involves:
- Animals Models of Disease states- Involves testing on animals which have been induced or already affected by similar conditions as of humans.
- Behavioural Studies- Tool to study behavioural results of drug
- Functional Imaging- Helps in tracing changes in metabolism, blood flow, chemical reaction, etc.
- Ex-vivo Studies- Experimentation on tissues in an artificial environment outside organism.
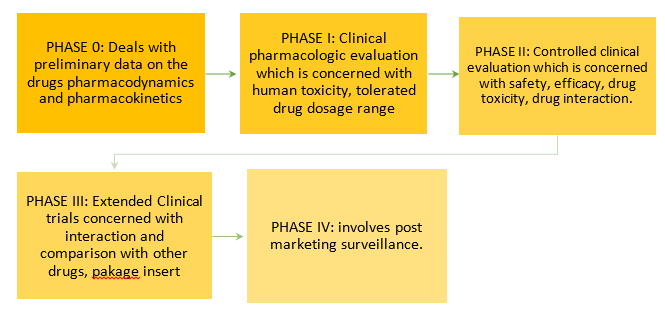
After the above process, drugs undergo a clinical trial which goes through the following phases:
Post clinical trials, if the drug is found to be completely suitable for human therapeutic use, it is sent for FDA or CDSCO approval. As the Food and Drug Administration/ Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation approves the drug, it is released in the market.
References:
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/273029/top-10-pharmaceutical-companies-sales-and-rundd-spending-in-2010/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead_compound
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drug_discovery