Science, due to its capacity to approve things through investigations, stands apart among different subjects; the experiments are done by the utilization of different laboratory equipment in controlled settings. While experimenting may be fun and fascinating, it is of utmost importance that the correct sort of lab supplies and equipment be utilized with extreme safety measures all together not to meet with any mishaps. There are 78 organs in a human body yet only 5 are considered to be vital. Just like that, several lab equipment assists in the day to day research and experiments but without these following most important equipment, the lab is just another room.
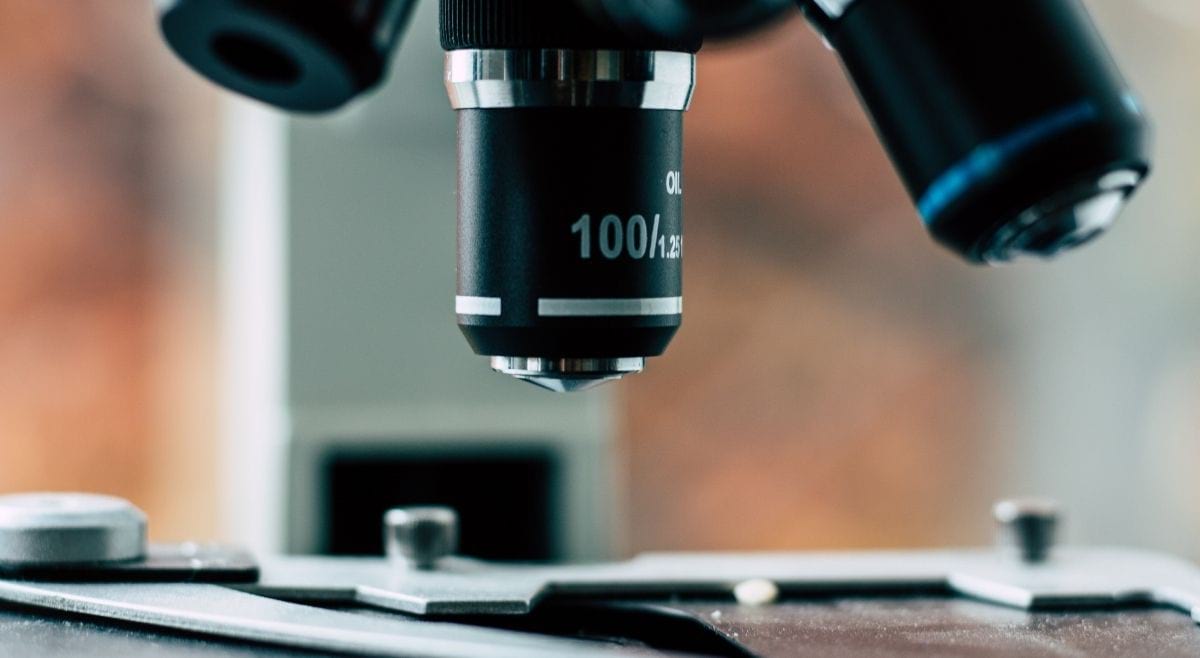
1. Microscope

Microscopes are the key to successful experiments and observations and no lab can fully operate without them. Microscopes are the foundation of any research or experiment in a laboratory that is required to try and complete even the most simple of actions like visualizing cells and microorganisms, preparing cell or fluid samples for visualization or testing, or dissecting microscopic specimens, you need a trustworthy microscope. Researchers and scientists use microscopes of different powers to observe organisms and samples more precisely that are high-powered, expensive and sensitive pieces of equipment. The smallest size an individual can observe with their naked eye is 0.2 mm that is equal to one ridge on their fingerprint. Microscopes can be grouped into various categories depending upon what interfaces with the sample/specimen to create the image and if they analyze the sample/specimen at the same time or through a scanning point.
2. Safety equipment
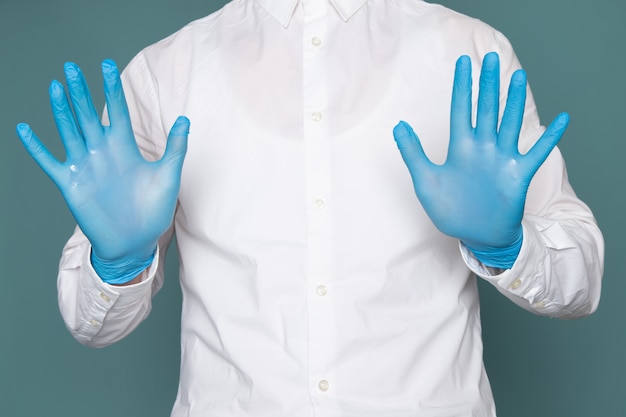

This set of equipment includes safety goggles, fire extinguisher, laboratory cloaks, and gloves. As it goes by the saying “safety comes first”, the best thing to do inside a lab is stick to the safety protocol 24*7 to avoid any kind of accident. Since all the laboratories have perilous substances and all sorts of chemicals it is necessary for all the working members to wear safety goggles. A lab cloak and gloves are a must while dealing with chemicals or biological substances to protect wearer’s clothing and exposed skin from hazardous substances or chemicals. A fire extinguisher should be handy when you are utilizing burners or flammable chemicals
3. Autoclave

An autoclave is a machine that sterilizes the lab instruments by killing the bacteria, viruses, and even spores present in the material put within the vessel utilizing steam under pressure. It is explicitly intended towards sterilizing lab applications used in laboratory, chemical, microbiology, food, and pharmaceutical industries by giving high-quality repeatable performance documentation for laboratory applications and quality confirmation measures. Autoclave sanitizes the materials by warming them up to a specific temperature for a particular timeframe which is usually 121 °C for 15 minutes. The autoclave is additionally considered as a steam sterilizer that is generally utilized in healthcare facilities and industries for different objectives.
4. Laminar air flow

Laminar Air Flow is a closed bench intended to forestall contaminations. It is generally comprised of stainless steel with no joints or gaps where spores may accommodate. Laminar hoods are outfitted with a small UV light system to sanitize the cabinet or the outside of the hood. It is instructed for the hoods to be turned on around 10-20 minutes prior to utilizing the laminar airflow. It is essential to turn off the UV light while working as there are chances that it might cause mutations and may cause sunburn on any uncovered skin and cataracts as well. It is needed to wipe down the inside of the hood with ethanol before and after using it and it’s also needed to keep the hood as clean as possible in light of the fact that this will meddle with the laminar stream air design. Laminar Air Flow has consistent air displacement in a streamline flow that goes through HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filter eliminating the contaminants from the air. All the equipment including tip boxes, stocks of sterile media, pipettes, culture vessels, test tubes, etc should be opened and put into use only inside laminar airflow. Even it is strictly instructed to prepare the culture media inside the hood as it can get contaminated and there wouldn’t be any result and conclusion.
5. Weighing balance

A weighing balance is an instrument that is utilized to calculate the weight or mass of any item. A weighing balance can be found in an assortment of sizes with different weighing limits and are basic instruments in research centers and laboratories. There are basically 2 types of weighing balances: Precision balance and analytical balance. Both are explicit kinds of weighing balances which determine very small masses than the normal or average scale. An analytical balance is most exact in light of the fact that it has higher readability, estimating to the closest 0.0001g. An analytical balance typically consists of a draught proof weighing chamber for accurate estimation of mass and is regularly utilized along with anti-vibration tables for better accuracy. On the other hand, a precision balance commonly measures the closest 0.1-0.01g yet has a higher limit. Both precision and analytical balances can measure capacities from 100 grams to kilograms. Because of their high accuracy and advanced technology, both are utilized explicitly in research labs to productively carry out experiments, for example, sampling amounts, density determination, quality control testing, purity analysis, etc.
6. Hot air oven

Hot air ovens are electrical instruments that use dry heat for sterilization. Dry heat sterilization is utilized on materials that won’t melt and on hardware that can’t be wet objects that are not flammable or objects that will not change its structure when presented to high temperatures. They utilize extremely high temperatures for a few hours to kill bacterial spores and microorganisms. For sterilizing objects, the hot air ovens utilize the process of conduction by heating the external surfaces of the object, which at that point assimilates the warmth and moves it towards the center of the object. The most utilized temperatures alongside the time period that hot air ovens require to sterilize materials are 170 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes, 160 degrees Celsius for 60 minutes, and 150 degrees Celsius for 150 minutes. The hot air ovens don’t need water and there isn’t a lot of pressure build-up inside it, in contrast to an autoclave, making them safer to work with. This likewise makes them more reasonable to be utilized in a laboratory atmosphere. They are smaller in size than autoclaves, however, equally effective.
7. Incubator

An incubator is a device that is an insulated and enclosed chamber that gives an ideal state of temperature, humidity, and other natural conditions required for the growth and development of microorganisms. It is a crucial laboratory instrument that is required to cultivate microbes in an artificial environment. The principle on which incubators work is thermo-electricity. Different types of incubators include:
BOD incubators: These are low-temperature incubators that are utilized for typically growing fungi (yeast and mold) as they need the low temperature to flourish. These are named so because in BOD testing there is a requirement of low temperature i.e. 20-25˚C.
Bacteriological incubators: It is utilized primarily in labs typically for the growth and development of microscopic organisms. A consistent temperature set by necessity is conceivable because it has a thermostat that keeps up the temperature. The majority of the incubators are programmable which needn’t bother with the experimentation temperature setting. They just hold the heating framework which keeps up the temperature for the development of microscopic organisms.
CO2 incubators: The primary objective behind a CO2 incubator is to keep up an ideal environment for cell growth and development, by giving CO2 control in a humidified environment with a steady temperature. The atmosphere created is natural to develop cell and tissue cultures which is the primary application of CO2 incubators.
8. Vortex

A vortex is an electrical device utilized for the mixing of small vials of fluid. A vortex comprises of an electric motor alongside a drive shaft fixed vertically to a cupped rubber piece. When the motor starts running the rubber piece rapidly oscillates in a circular movement. At the point when a test tube or other container is pressed onto the rubber cup, the movement is communicated to the fluid inside and a vortex is made. Most vortex blenders are planned with 2 or 4-plate designs, have variable speed settings running from 100 to 3,200 rpm, and can run continuously.
9. Refrigerator

Refrigerators are utilized for storage applications in different laboratories. They assure an even temperature throughout the chambers by forced air course framework. Refrigerators provide value and protect your samples. The refrigerators in a laboratory are utilized for the cooling of samples/specimens for preserving them for further use. They can be utilized to store blood plasma and different blood items, vaccines, and other clinical or drug supplies. These refrigerators are required to be absolutely hygienic and reliable. Laboratory refrigerators keep up a constant temperature to reduce the danger of bacterial contamination and explosions of volatile materials.
10. Water bath

A water bath is one of the important equipment in a laboratory, which is utilized to incubate samples submerged in water at a consistent temperature. It is made from a compartment loaded up with heated water. It comes in different designs, sizes, and measurements. Water baths have a wide range of applications including heating reagents, corrosion tests, bacteriological examinations, sample thawing, incubation of cell cultures, enabling specific chemical reactions to occur at higher temperatures. Most of them have an advanced or an analogue interface to permit the users to set an ideal temperature.
11. Centrifuge

A centrifuge is an instrument that segregates particles of a solution as per their shape, size, rotor speed, density, or viscosity of the medium under gravitational force. A centrifuge is basically driven by an electric motor that keeps an object in a rotational motion in a fixed axis. The principle behind centrifugation is sedimentation. In a solution, the particles having a greater density than the solvent settle down at the bottom and the lighter particles float to the top. The greater the difference in density, the faster they move. There are different types of centrifuges depending on the size, the desired speed, and the sample capacity such as benchtop centrifuge, continuous flow centrifuge, gas centrifuge, high-speed centrifuge, low-speed centrifuge, microcentrifuge, etc.
12. Micropipette and microtips


One of the most broadly utilized methods of any Biology, Chemistry, and Physics laboratory is liquid handling. While it is very simple and hassle-free to deal with larger volumes of fluids by utilizing lab apparatus like a beaker, graduated cylinder, volumetric flasks, etc, working with the minute or smaller volumes of fluid gets problematic, tricky, and often dreary. For the handling of small volumes of liquid, micropipette is the instrument that is utilized in the research laboratories. A micropipette can vary depending upon its size that can range from P2 (0.2-2 uL), P10 (1-10 uL), P20 (2-20 uL), P100 (20-100 uL), and P200 (20-200 uL) to P1000 (100-1000 uL). The fluids are never drawn directly into the shaft of the micropipette rather a disposable tip is attached manually to the shaft of the micropipette. All micropipettes have a volume adjustment dial at the top. In order to prevent contamination new tip is utilized for every sample, discarding the older one. The most fundamental feature of a micropipette tip is its high quality, whether you’re searching for low retention, filtering, gel loading, or mixing of samples thoroughly, ensure that the tip will work as required and as exact as your micropipette.
13. Glassware and Plasticware
Laboratory glassware and plasticware form the basic containers in which experiments are performed, and hence form a vital equipment of the science laboratory. Some of the most important types of glassware and plasticware are noted here.
Beaker

A beaker is a cylindrical container made of glass and that has a flat bottom. Beakers are designed in such a way that they have a spout to ease the pouring. It is the workhorse equipment in any laboratory. Beakers help in storing of samples for later use, heating of sample over a flame, measuring and stirring fluids, or collecting liquids.
Test tubes and test tube rack

A test tube, otherwise called a culture/sample tube, is a typical type of lab instrument comprising of a finger-like length of glass or clear plastic tubing, open at the top, and shut at the base. In case the sample is required to be put in a centrifuge or if any addition to the existing sample is required, then the sample is likely to be put inside a test tube.
Test tube racks are utilized in labs to hold numerous test tubes simultaneously. They are most regularly utilized when different various solutions are expected to work with all the while, for safety reasons, for safe stockpiling of test tubes, and to facilitate the transport of numerous tubes safely.
Conical flasks

A conical flask is also known as an Erlenmeyer flask. It comprises a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck. It varies from a beaker in terms of having a narrow neck and tapered body. They might be built from glass or plastic, depending on the application in a broad range of volumes. These flasks are mainly utilized to prepare microbial cultures, sterilization of cell cultures, and mixing the content of a solution or mixture.
Measuring cylinder

Also known as a graduated cylinder, a measuring cylinder is a standard piece of laboratory equipment utilized for the measurement of a volume of liquid. As the name suggests, it is narrow and cylindrical in shape and each line marked on it shows the amount of liquid that is measured. It can be built from glass or plastic, depending on the application. The volume of a liquid that needs to be measured is calculated by looking at the top of the liquid from the side and reading the marks from the meniscus of the fluid. These are explicitly designed to make precise volume measurements.
Petri dish

A Petri dish is a shallow lidded dish that is transparent and is utilized by the researchers and scientists to hold the medium in which the cells are cultured. It is the most well-known kind of culture plate. For culturing any sample, a petri dish consisting of the culture medium is inoculated/ smeared and pressed onto the medium.
Glass slide
It is a flat piece of glass upon which sample cells are smeared, fixed (so that the components of the cell won’t get displaced from its place), covered with a coverslip, and then viewed under a microscope.
Coverslips

Coverslips are flat and ultra-thin pieces of glass typically 75 by 26 mm (3 by 1 inch) and about 1 mm thick and are utilized for holding objects to examine under a microscope.
Centrifuge tubes

Centrifuge tubes are utilized to hold fluids during centrifugation, which isolates the sample into its parts by rotating rapidly in a fixed axis. The majority of the centrifuge tubes have bottoms that are conical in order to gather any solid or heavier parts of the sample that is being centrifuged. They are designed in such a way that it has the capability to withstand the centrifugal pressure that builds up during the process. They can be found in a broad range of sizes, styles, and materials.
14. Laboratory Tools
While the list of tools needed can very from the kind of work being carried out, some of the common ones like bunsen burner, spirt lamps, tripod stand, spatula, tongs, inoculating loop, etc are needed in almost every lab.
Bunsen burner

A Bunsen burner is utilized to create a single continuous flame by blending gas with air in a controlled manner. The gas to air ratio that is blended together can be adjusted manually which permits the user to control the size, intensity, and temperature of the flame. The applications of a Bunsen burner include heating, sterilization, and combustion.
Tripod stand

A tripod is a three-legged equipment generally utilized to carry out experiments in laboratories. It is utilized as a stage to support and hold containers like conical flasks and beakers during experiments. Its height can be easily adjusted according to individual requirements. Tripods can hold any type of equipment efficiently and are usually made of light metals which make them light-weighted. They are portable and can be transferred and folded easily, making them appropriate for laboratory facilities with confined space.
Spatula

A spatula is a flat, wide, flexible blade that is utilized to blend, spread, and transfer materials. Spatulas are made of stainless steel that helps to scrap, transfer, or apply powders and paste such as chemicals or nutrient medium powders. Many of the spatulas are even resistant to acids, bases, and other corrosive chemicals. They are sturdy, reliable, and cost-effective.
Tongs

Tongs are utilized to remove the lids from containers, pick up small items from a reaction container, and transfer evaporating crucibles. Beaker tongs are utilized to carry beakers, evaporating dishes, or conical flasks. These tongs have an appearance just like a scissor except the two sharp blades that a normal scissor has is supplanted with two princers or metal parts having the tips forked out or serrated. They are typically produced from sturdy metals like steel, tempered steel, nickel-plated steel, cadmium-plated steel, etc.
Rubber bulbs

Rubber bulbs serve as a source of vacuum to fill reagents by pipette or Pasteur pipette and it also controls the flow of fluid from the dropping bottle. The contact of the mouth to the chemicals can be avoided by utilizing rubber bulbs. These rubber rods come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors.
Inoculating loop

It is also called a smear loop. An inoculating is one of the most important tools utilized in laboratories that help in smearing, streaking, or taking an inoculum from, a culture of microorganisms.
Mortar Pestle

The mortar and pestle are utilized to crush or grind ingredients. It usually transforms ingredient into a fine powder and paste. Mortar is a thick wall shaped bowl and pestle is a structure that is blunt end rod-like. It has a rough touch that assists in holding the ingredient against the pestle. The strikes from pestle apply some measure of pressure which is sufficient to separate the ingredients into semi-solid constituents. The outcome of this is fine powder or paste.
Above mentioned are some of the most crucial equipment of laboratory that can be found in any laboratory in the world. The lab equipment should only be bought from quality manufacturers assuring good performance, minimal maintenance cost, and operator safety.
Reference:
https://www.dummies.com/education/science/biology/basic-equipment-used-in-biology-experiments/
//blog.biomall.in/essentials-for-setting-up-a-science-laboratory/
https://international-scientific.com/top-10-essential-biology-lab-equipment-part-1/
http://eblogin.com/5-important-pieces-lab-equipment/
https://scienceequip.com.au/blogs/news/list-of-science-equipments-a-laboratory-must-have