In multiplex real-time PCR (qPCR), scientists amplify two or more target genes in the same reaction, using the same reagent mix. Multiplexing allows scientists to overcome limitations for myriad applications.
First and foremost, multiplexing enables scientists to conserve valuable samples used in a quantitative assay, which is especially important for research involving difficult-to-obtain specimens. In a single qPCR experiment, only the gene of interest or the control is amplified in each well. If each assay is performed in triplicate, researchers need to divide a sample into multiple wells to measure gene expression, limiting the number of genes that can be tested when using a sample in short supply. Scientists overcome these limitations by amplifying multiple genes in the same reaction. Additionally, researchers reduce the cost and time required to perform qPCR because they use fewer reagents per experiment and can run experiments and analyze results more quickly. Because pipetting errors may also be minimized in one reaction versus several, researchers may also benefit from improved precision when performing multiplex qPCR versus single assays.
Applying multiplex qPCR in research and industry
Multiplex qPCR is a good choice for various applications:
Gene Expression Analysis: In gene expression analysis, researchers study the occurrence or activity of a gene product from its coding gene. This provides a sensitive indicator of biological activity; changing gene expression patterns reflect changing biological processes. Multiplexing is readily expandable to capture additional loci or to cover additional species.
SNP Genotyping: Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations between members of a species. Multiplexing qPCR assays for SNP genotyping increases efficiency by saving samples, reagents, and time.
Copy number variation: Copy number variation (CNV) occurs when sections of the genome repeat and the number of repeats varies between individuals. The human genome contains many CNVs, some of which are involved in complex diseases; many others cause inherited diseases. Scientists use multiplex qPCR to research multiple CNVs at the same time, facilitating research into many diseases.
Genetically modified plant detection: The aim of genetically modified organism (GMO) monitoring is to detect potential adverse effects of GMOs on human health and the environment and to mitigate spread if necessary. PCR assays for detecting GM plants often target the P35S or TNOS DNA sequences. However, because the P35S promoter is derived from the Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV), these detection assays can yield false-positive results from non-GM plants infected by this naturally-occurring virus. Multiplexing allows scientists to distinguish CaMV-infected plants from GM plants in a single reaction.
Rapid pathogen identification: Molecular tests such as qPCR may enable early adjustments to antimicrobial therapy and complement blood culture for critically ill patients. Scientists can use multiplex qPCR to test for several potential pathogens in the bloodstream at the same time, which may expedite patient treatment.
Epidemiology and drug efficacy monitoring: Accurate quantitative assessment of various parasite or microbe infections is key to interpreting epidemiologic data. It also aids in monitoring large-scale treatment efficacy studies. Multiplex qPCR assays assist researchers in tracking the prevalence, intensity, and response to treatment for infections on a far wider scale than single assays.
Multiplexing made simple
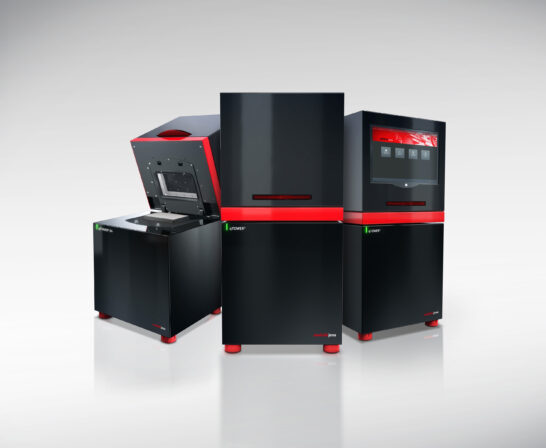

Analytik Jena’s qTOWER³ product family achieves unique flexibility with its proven filter module equipment, which can be freely configured and expanded at any time and enables up to six-fold multiplexing. For any qPCR application, researchers can reduce repeat analyses, increase analysis speed, and reduce the cost per sample using qTOWER technology. The thermal cycler provides state-of-the-art heating technology and temperature homogeneity, which returns more accurate results.
To know more about qTOWER, please visit here